1. What Is Food Packaging Material?
Food packaging material refers to any substance or system that comes into contact with food during processing, storage, transportation, or distribution, such as plastic film, metal cans, glass jars, and cardboard . Its primary purpose is to protect food from contamination, preserve freshness, ensure safe transportation, convey product information, and enhance brand image. Choosing the right food packaging material is not only about ensuring food hygiene and safety, but also about meeting international standards and consumer expectations .
Low-priced packaging materials can temporarily solve your production needs, but food packaging materials are developing towards environmental protection and recycling. It is imperative to use safe and environmentally friendly packaging materials for long-term development.
2. Classification of food packaging materials
2.1 Plastic

- Applications : Beverages, dairy products, processed foods and snacks.
- Advantages: PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PS are commonly used plastics for bottles, trays, films, and packaging bags. They are flexible, lightweight, and low-cost.
- Disadvantages: Migration of additives or residual monomers in plastics remains a safety concern. Recycling rates vary by region, and the reuse or recycling of many plastics, such as PS or PVC, is challenging.
2.2 Metal

- Applications: Aluminium, tinplate and steel , widely used in cans, foils and lids.
- Advantages: Effective barrier to oxygen, moisture and light. Internal coating prevents corrosion or chemical reactions. Metal packaging generally has a long shelf life and is highly recyclable at established global recycling rates.
2.3 Glass
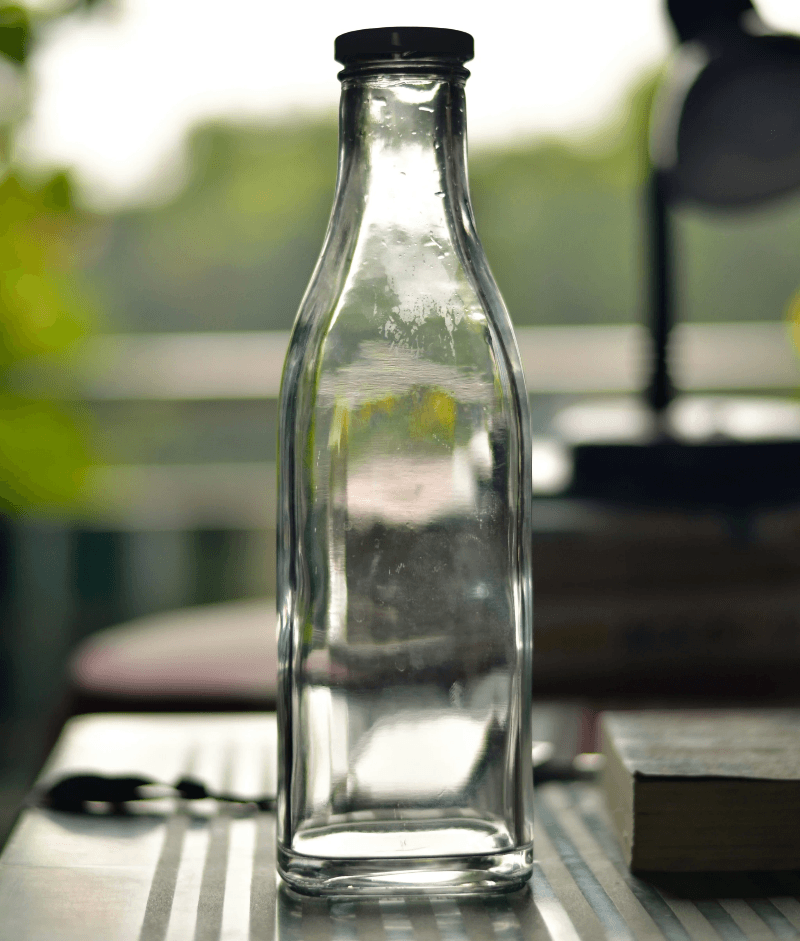
- Applications: Commonly found in sauces, baby foods, condiments and premium beverages.
- Advantages: Glass is chemically inert and retains flavors and aromas without the risk of migration.
- Disadvantages: Although glass can be recycled infinitely, it is heavy and fragile, and has a greater impact on the environment during transportation.
2.4 Paper and fiber packaging

- Applications: Cardboard, paperboard, molded pulp, kraft paper and paper packaging. Commonly used in dry goods, cartons, pallets and secondary packaging.
- Disadvantages: Often coated with polyethylene, wax, or foil to protect against moisture or oil, which can affect recyclability.
2.5 Biodegradable and compostable materials
- Applications: Best suited for dry, �short-shelf-life items such as snacks and takeout packaging.
- Advantages: PLA (polylactic acid), cellulose film, starch blend and molded bagasse are designed to biodegrade under industrial composting conditions.
- Disadvantages: Composting infrastructure and consumer understanding are still limited in many areas.
3. Safety and regulatory requirements
The global food packaging industry is undergoing a major transformation towards environmental protection, safety and intelligence.
EU food packaging regulations are centered around environmental protection and the circular economy, requiring materials to be recyclable, biodegradable, or reusable. Plastics must comply with the migration limits set by (EU) No 10/2011, and single-use plastics (such as straws and cutlery) must be phased out. Recycled plastics must undergo rigorous certification (such as (EU) 2022/1616) to ensure they are free of contamination risks. The PPWR regulation, effective in 2025, will mandate that all packaging be recyclable. In recent years, US states have also been tightening restrictions on PFAS and BFAs. While emerging markets primarily rely on low-cost packaging, they are gradually aligning with international standards . Given this trend, companies need to plan ahead to prepare for future regulatory escalation .
4. Packaging materials and brand/consumer perception

In today's highly competitive food market, packaging materials have surpassed their traditional protective functions and become an important medium for conveying brand value and connecting with consumers emotionally.
From a consumer psychology perspective, different packaging materials create distinct brand perceptions. Glass and metal, with their texture and durability, naturally project a high-end, professional brand image, often seen in premium wines and high-end foods. Natural cardboard or compostable materials, on the other hand, signal a brand's environmental awareness. Notably, packaging details such as the tactile experience (such as a frosted finish) and the opening method (such as a magnetic closure) can significantly enhance consumer perception of quality and brand loyalty.
A successful food packaging strategy should be a perfect fusion of material science, consumer psychology and brand narrative. It should not only ensure functional needs, but also convey the core brand value through material language, ultimately establishing an emotional connection of "love at first sight" and lasting brand loyalty in the minds of consumers.
5. How to choose suitable food packaging materials
To choose the best food packaging material for your product , consider:
- Food type – liquids, dry goods, frozen foods, fatty foods, acidic products
- Barrier requirements - moisture, oxygen, and light protection
- Shelf life - stable at room temperature, refrigerated, and frozen�
- High temperature resistance - suitable for hot filling, steaming and microwave ovens�
- Compliance - ensure FCS authorization, compliance documents (FDA, EU)
- Sustainability Goals – Recycling or composting regulations in your region
- Brand positioning – premium feel, environmental message, custom printing capabilities
- Process compatibility – suitable for your filling/sealing machinery and format
6. Summary
Choosing the right food packaging material means striking a balance between safety, regulations, product performance, environmental impact, and brand perception. Each material category—plastic, metal, glass, paper, or compostable—offers unique advantages and challenges that must be aligned with your product type and market demands. Ensure regulatory compliance documentation and supplier quality, and always consider how material selection impacts consumer trust and sustainability goals.
Contact us for customized guidance on selecting compliant food packaging solutions . We offer FDA/EU certifications, custom designs, and discounts on first-time OEM packaging projects .
